Introduction to Logarithmic Differentiation YouTube
Derivative of y = ln u (where u is a function of x). Unfortunately, we can only use the logarithm laws to help us in a limited number of logarithm differentiation question types. Most often, we need to find the derivative of a logarithm of some function of x.For example, we may need to find the derivative of y = 2 ln (3x 2 − 1).. We need the following formula to solve such problems.

Example 31 Derivative of a^x Chapter 5 Class 12 Logarithmic Diff
Solution: Given function: \ (\begin {array} {l}y = e^ {x^ {4}}\end {array} \) Taking natural logarithm of both the sides we get, ln y = ln e x4 ln y = x 4 ln e
Derivatives of Logarithmic Functions (Fully Explained!)
Show Solution Example: Using Properties of Logarithms in a Derivative Find the derivative of f (x) =ln( x2sinx 2x+1) f ( x) = ln ( x 2 sin x 2 x + 1) Show Solution Try It Differentiate: f (x)= ln(3x+2)5 f ( x) = ln ( 3 x + 2) 5. Hint Show Solution Watch the following video to see the worked solution to the above Try It.

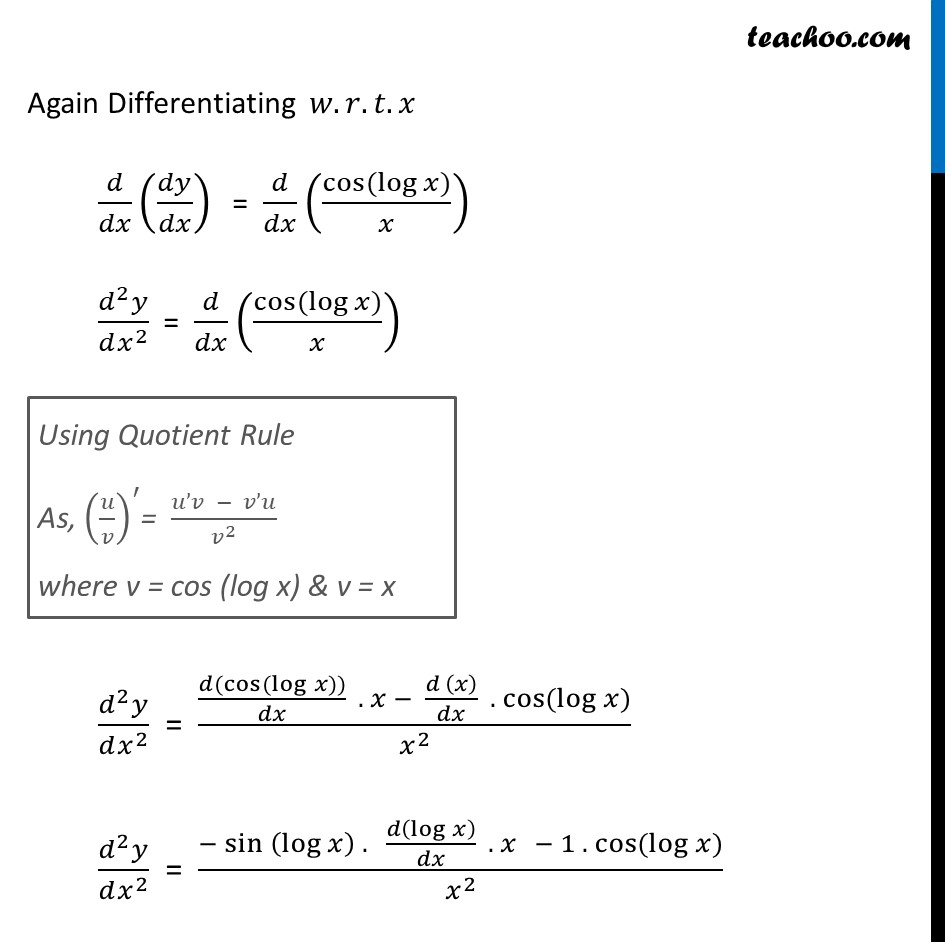
Ex 5.7, 9 Find second order derivatives of log (log x)
Free derivative calculator - differentiate functions with all the steps. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph

Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x
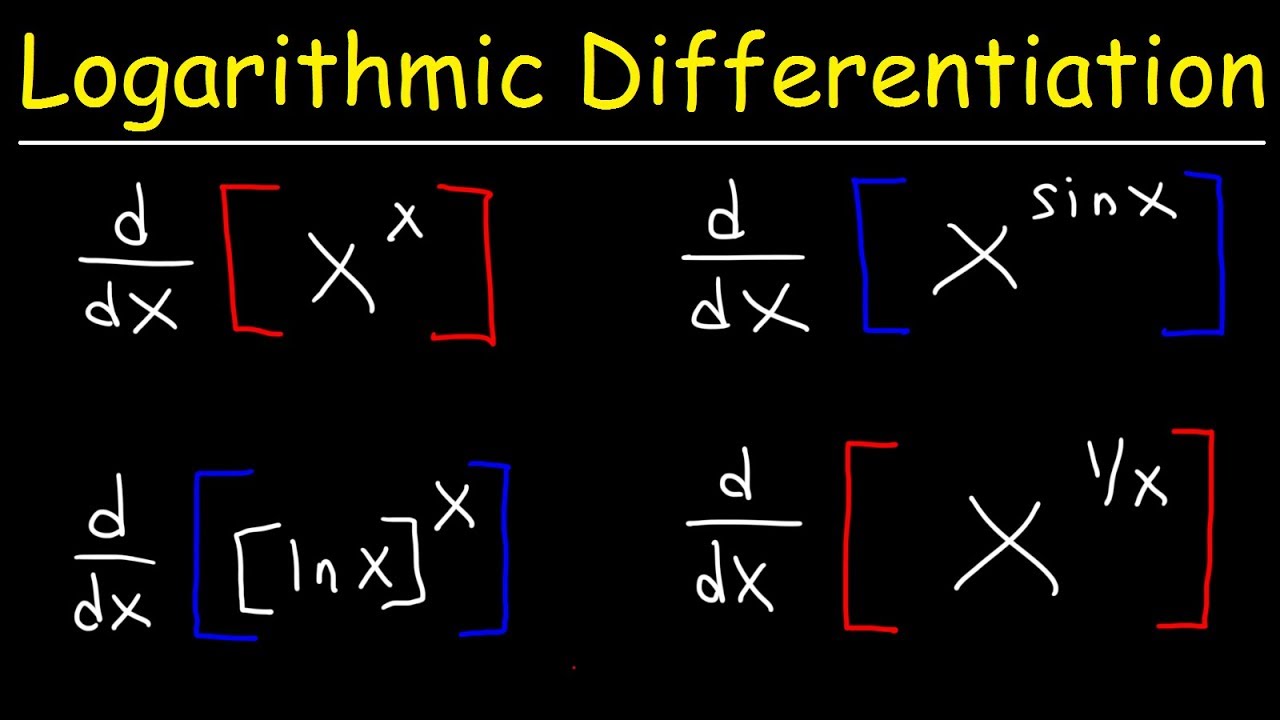
These functions require a technique called logarithmic differentiation, which allows us to differentiate any function of the form \(h(x)=g(x)^{f(x)}\). It can also be used to convert a very complex differentiation problem into a simpler one, such as finding the derivative of \(y=\dfrac{x\sqrt{2x+1}}{e^x\sin^3 x}\).

Question Video Using Logarithmic Differentiation to Differentiate a
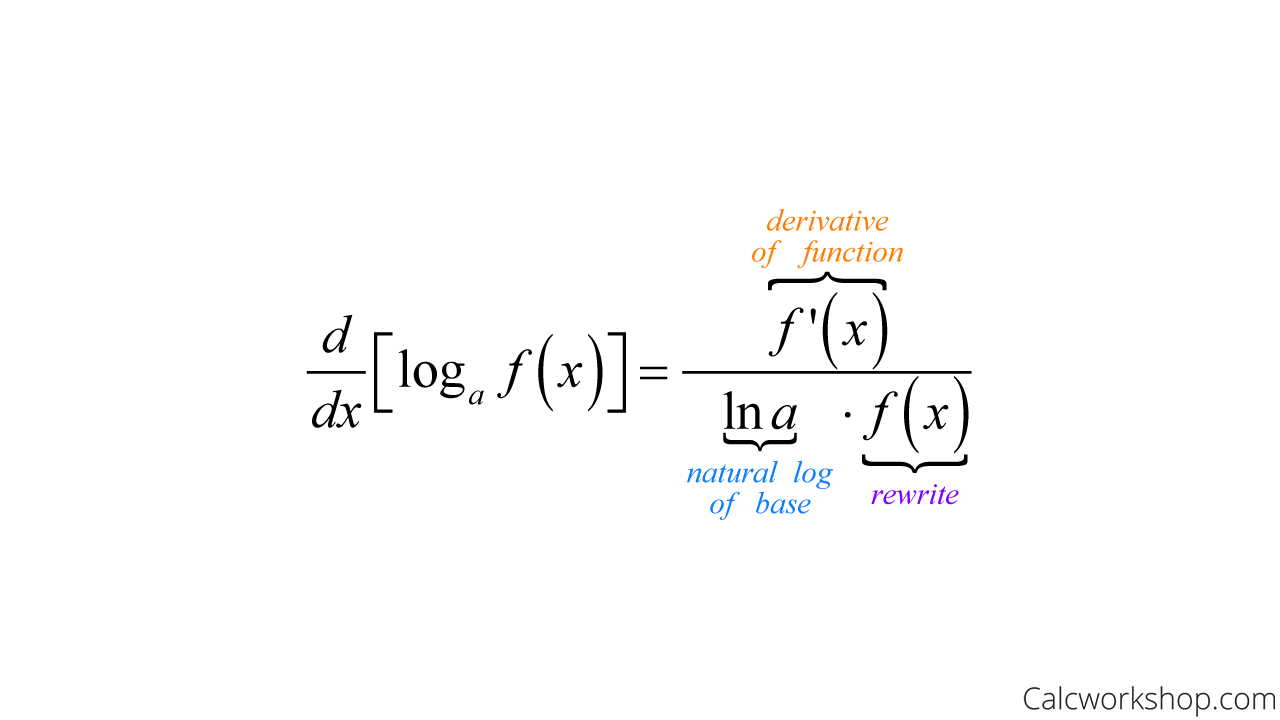
Differentiation of log x. Differentiating loga x is easy and can be done using first principles. Assuming it is a log function to the base number a. d / dx loga x = 1 / xln a. The derivative of loga x is therefore 1 / xln a.

07 Differentiation of log x to the base a by first principle
Logarithmic differentiation is based on the logarithm properties and the chain rule of differentiation and is mainly used to differentiate functions of the form f(x) g(x)· It helps in easily performing the differentiation in simple and quick steps. The functions which are complex and cannot be algebraically solved and differentiated can be differentiated using logarithmic differentiation.
Derivative of log x base a modernpsado
more. By the change of base formula for logarithms, we can write logᵪa as ln (a)/ln (x). Now this is just an application of chain rule, with ln (a)/x as the outer function. So the derivative is -ln (a)/ ( (ln (x))²)· (1/x). Alternatively, we can use implicit differentiation: given y=logᵪ (a), we write x^y=a.

Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x
This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into derivatives of logarithmic functions. It explains how to find the derivative of natural loga.

Ex 5.7, 4 Find second order derivatives of log x Teachoo
Now, practice with a few examples. Example 1: What is the derivative of ln (2x)? Notice that the chain rule can be used here to find the derivative. In this case, the inside function is 2x, and.
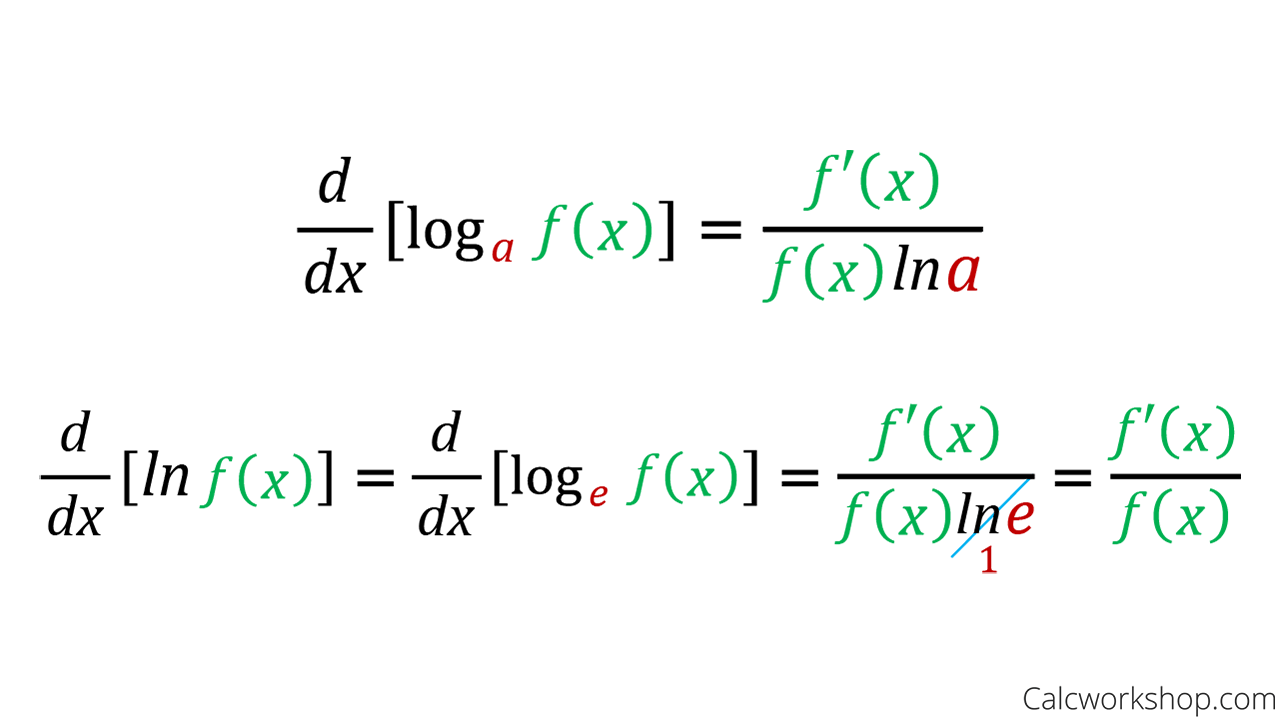
Derivatives of Logarithmic Functions
Derivatives in maths enable the calculation of function change rates in terms of variables. The function defined by y = loga(x) ( x > 0) where x = ay, a > 0, a ≠ 1 is called the logarithm of x to the base a. The derivative of loga(x) is 1 xln ( a). The derivative of loga(x) is denoted by d dx(loga(x)) or (loga(x)).
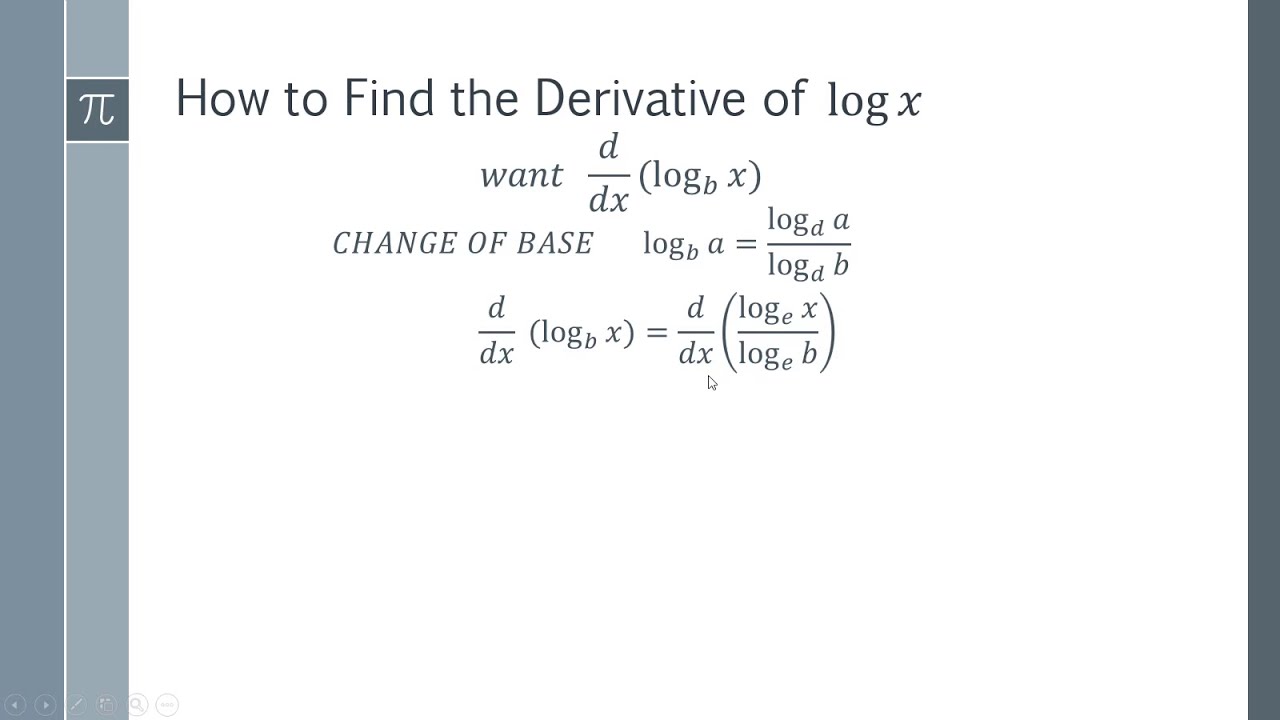
How to find the derivative of logx YouTube
What is the Derivative of log x? The derivative of logₐ x (log x with base a) is 1/ (x ln a). Here, the interesting thing is that we have "ln" in the derivative of "log x". Note that "ln" is called the natural logarithm (or) it is a logarithm with base "e". i.e., ln = logₑ.
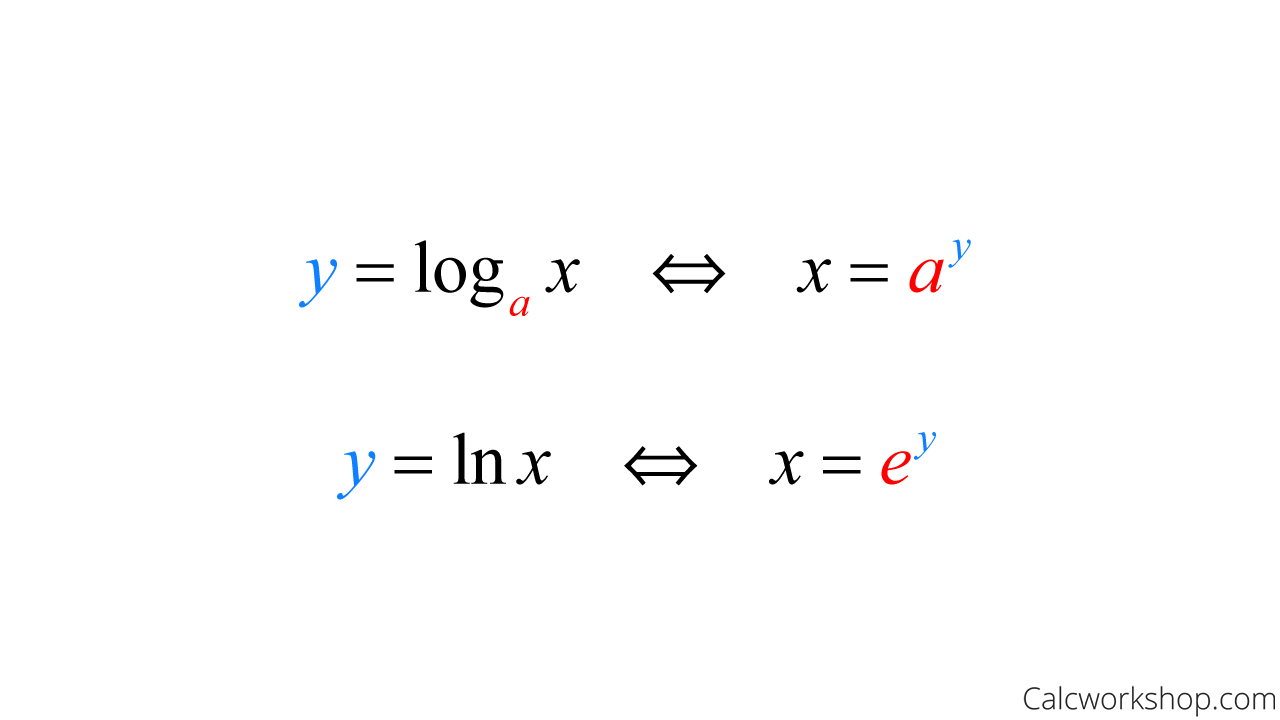
Logarithmic Function Formula
Solution 1: Use the chain rule. Let f (x) = \ln x f (x) = lnx and g (x) = 5x g(x) = 5x. Then we are asked to find ( f \circ g ) ' (f ∘g)′. Using chain rule, we know that ( f \circ g ) ' = ( f' \circ g) \times g' . (f ∘g)′ = (f ′ ∘g)×g′.

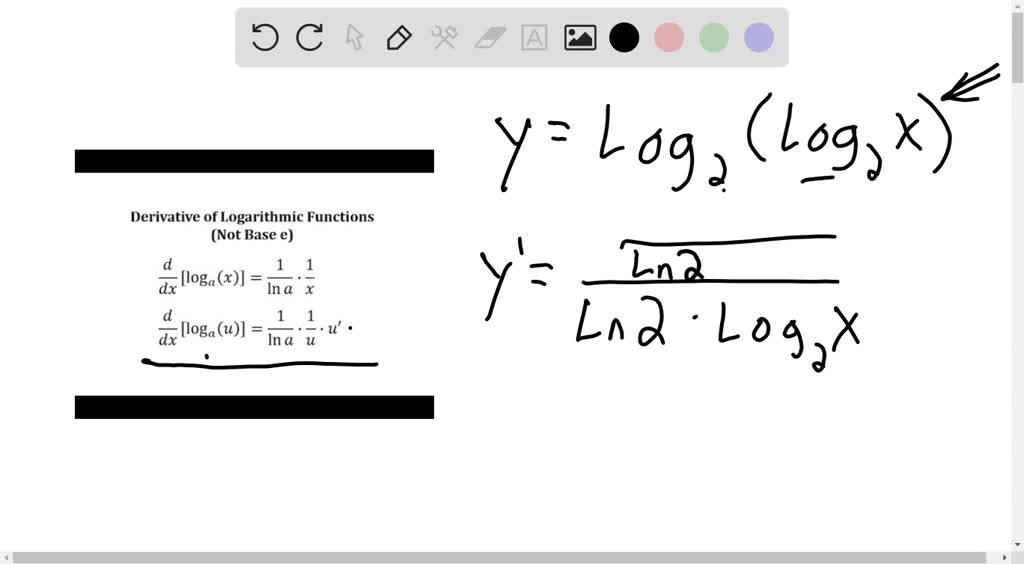
Differentiation of log (log x) Chain Rule Teachoo Ex 5.4
These functions require a technique called logarithmic differentiation, which allows us to differentiate any function of the form \(h(x)=g(x)^{f(x)}\). It can also be used to convert a very complex differentiation problem into a simpler one, such as finding the derivative of \(y=\frac{x\sqrt{2x+1}}{e^x\sin ^3x}\). We outline this technique in.
Second derivative of log x clubsdase
3.6: Derivatives of Logarithmic Functions. Page ID. As with the sine, we do not know anything about derivatives that allows us to compute the derivatives of the exponential and logarithmic functions without going back to basics. Let's do a little work with the definition again: d dxax = lim Δx → 0ax + Δx − ax Δx = lim Δx → 0axaΔx −.

Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x
Show Solution So, as the first example has shown we can use logarithmic differentiation to avoid using the product rule and/or quotient rule. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. y =(f (x))g(x) y = ( f ( x)) g ( x) Let's take a quick look at a simple example of this.